Product docs and API reference are now on Akamai TechDocs.
Search product docs.
Search for “” in product docs.
Search API reference.
Search for “” in API reference.
Search Results
results matching
results
No Results
Filters
How to Install and Configure Pixelfed
Traducciones al EspañolEstamos traduciendo nuestros guías y tutoriales al Español. Es posible que usted esté viendo una traducción generada automáticamente. Estamos trabajando con traductores profesionales para verificar las traducciones de nuestro sitio web. Este proyecto es un trabajo en curso.
Pixelfed is a decentralized federated application that allows users to share photos, art, and videos. This guide explains how to install and configure Pixelfed and provides details about all prerequisites.
What is the Federated Web?
Mastodon, Pixelfed, and other applications make up the federated web, also known as the Fediverse. The Fediverse is a collection of independent yet interconnected servers. Federated applications are said to be decentralized because there is no central server or administrative hierarchy. Each server is typically self-hosted, but users can join any server. In many cases, a user account can cross server boundaries and access or post content to multiple servers. The Fediverse is frequently used to host web content, including websites, social networks, and blogs.
What is Pixelfed?
Pixelfed is a decentralized and open-source alternative to corporate photo-sharing sites such as Instagram. Users can self-host their own Pixelfed account or join one of many community servers. Pixelfed is free to download and use and does not have any ads. Pixelfed maintains privacy-friendly policies and does not store or sell user data.
Some of the main features of Pixelfed are as follows:
- Chronological feeds that are free from algorithmic intrusion
- Support for the ActivityPub Protocol to allow users to follow and interact with Mastodon posts from their Pixelfed account
- Mobile support
- Photos can be grouped into albums
- A wide selection of filters
- Support for comments, direct messages, and likes
- The “Stories” feature for time-limited sharing
- A wide range of privacy and safety-oriented features. Users can manually approve followers, add follower-only posts, mute/block accounts, report accounts, and disable comments.
For a more complete list of Pixelfed features, see the Pixelfed features page .
Before You Begin
If you have not already done so, create a Linode account and Compute Instance. See our Getting Started with Linode and Creating a Compute Instance guides.
Follow our Setting Up and Securing a Compute Instance guide to update your system. You may also wish to set the timezone, configure your hostname, create a limited user account, and harden SSH access.
Assign a domain name for the Pixelfed server and point it at the IP address of the server. For information on domain names and pointing a domain name to a Linode, see the Linode DNS Manager guide .
(Optional) To allow Pixelfed to send emails, enable email on the Linode server.
sudo. If you are not familiar with the sudo command, see the Linux Users and Groups
guide.How to Configure the Server to Support Pixelfed
Pixelfed requires a large number of supporting applications, including a full LAMP or LEMP stack. It also requires the extensive use of composer and artisan installation scripts.
The following instructions explain how to install Pixelfed on Ubuntu 22.04, but are generally applicable for most Linux distributions.
Install the LEMP Stack and Other Prerequisites
Pixelfed requires a web server, database, and the PHP programming language to operate. The Linux stack can use either Apache or NGINX for the web server. This guide provides instructions for NGINX, which integrates more easily with Pixelfed. This guide points out the sections where the Apache installation method differs, but does not provide detailed Apache instructions. For the database, either MariaDB or MySQL can be used. In both cases, the database configuration is the same. To install a LEMP stack for Pixelfed, follow the steps below:
Install the NGINX web server.
sudo apt install nginxUse
systemctlto confirm NGINX isactive.sudo systemctl status nginxnginx.service - A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Tue 2022-11-29 13:01:56 UTC; 15s agoInstall the MariaDB database.
sudo apt install mariadb-serverConfigure the
ufwfirewall to accept NGINX connections. Allow theNginx Fullprofile to permit both HTTP and HTTPS connections. This profile is mandatory because Pixelfed requires HTTPS for uploads.sudo ufw allow OpenSSH sudo ufw allow in "Nginx Full" sudo ufw enableNote After installing Pixelfed and enabling HTTPS, consider changing theufwprofile toNginx HTTPS. This setting limits firewall access to HTTPS traffic only.Verify the firewall settings using the
ufw statuscommand.sudo ufw statusStatus: active To Action From -- ------ ---- OpenSSH ALLOW Anywhere Nginx Full ALLOW Anywhere OpenSSH (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) Nginx Full (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)Visit the IP address of the webserver to ensure web access is operational. The browser should display the default NGINX welcome page, including the message “Welcome to nginx!”.
Note Use the Linode Dashboard to determine the address of the Linode.Run the
mysql_secure_installationtool to increase the security of the database.sudo mysql_secure_installationThe script prompts several responses. It is not necessary to switch over to Unix socket authentication or change the root password. Answer
Yto the remaining questions.Remove anonymous users?Disallow root login remotely?Remove test database and access to it?Reload privilege tables now?
Install PHP including all supporting packages.
sudo apt install -y php-gd php-bcmath php-ctype php-curl php-exif php-iconv php-intl php-json php-imagick php-services-json php-mbstring php-tokenizer php-xml php-zip php-mysql php-fpmPixelfed requires some additional packages, including image processing utilities. The following command installs the Redis database and its PHP package, supporting utilities such as
gitandcomposer, and image processing packages includingjpegoptim.Note Some utilities might already be installed on the server.sudo apt install -y php-redis ffmpeg redis git libgl-dev gcc libc6-dev libjpeg-dev make jpegoptim optipng pngquant graphicsmagick gifsicle composer zip unzip
pixelfed user to run Pixelfed. Remember to switch to this user when installing and configuring the application. See the Pixelfed Prerequisites information
for more information.Configure the Database and PHP
After installing the LAMP/LEMP stack and the other mandatory packages, more configuration is still required. The steps in this section explain how to configure the database and virtual host to support Pixelfed.
Log in to the database as
root.sudo mysql -u root -pCreate the
pixelfeddatabase and thepixelfeddatabase user. Flush the privileges and exit the database. ReplacePASSWORDwith a unique secure password.CREATE DATABASE pixelfed; CREATE USER 'pixelfed'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'PASSWORD'; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON pixelfed.* TO 'pixelfed'@'localhost'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES; EXITUpdate the
php.inifile with new settings for Pixelfed. This file can be found at/etc/php/<php_version>/fpm/php.ini, wherephp_versionis the release of PHP used on the server. For instance, if PHP8.1is installed, the file,php.inican be found at/etc/php/8.1/fpm/php.ini. To check which version of PHP is installed, you can use the commandphp -v. Make the following changes to the file:- Set
post_max_sizeto the maximum size for any submission. The default is8M, but this might not be large enough for high-quality photos or animation. - Ensure
file_uploadsis set toOn. - The value of
upload_max_filesizemust be<=the value ofpost_max_size. - Set
max_file_uploadsto the maximum number of attachments for any upload. The default is20. - Increase
max_execution_timeto 600.
Note These settings are found in different sections of the file. In thevieditor, use the/key to search for the name of the setting.- File: /etc/php/8.1/fpm/php.ini
1 2 3 4 5max_execution_time = 600 post_max_size = 8M file_uploads = On upload_max_filesize = 6M max_file_uploads = 20
- Set
Configure a Virtual Host and HTTPS Support
The next step is to create a virtual host file for the Pixelfed domain. A virtual host allows for the configuration of domain-specific settings. Pixelfed requires HTTPS support, which can be enabled using the Certbot application. This guide covers the main steps required to install and use Certbot. For more detailed information about Certbot, Let’s Encrypt certificates, and HTTPS, see the Linode guide to Using Certbot on NGINX .
Create a
/var/www/html/domain_namedirectory for the Pixelfed site. In the following command, replaceexample.comwith the actual name of the domain.sudo mkdir -p /var/www/html/example.comCopy the default site configuration file to the
sites-enableddirectory. This ensures the formatting is correct and all essential fields are included. Use the domain name in place ofexample.com.sudo cp /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default /etc/nginx/sites-available/example.com.confEdit the site’s
.conffile. Delete the existing server configuration all the way to the lineVirtual Host configuration for example.comand uncomment the remaining lines. All further changes must be made inside the code block beginning with theserver. Change theserver_nameandrootfields inside theserverblock to reference the Pixelfed domain. In the following example, replaceexample.comwith the actual domain name. The remaining changes can be made after HTTPS is enabled.Note When Pixelfed is installed inside the/var/www/html/domain_namedirectory, it creates a newpublicsubdirectory. Therootvariable must point to this directory. For Apache, add this configuration to/etc/apache2/sites-available/example.com.confinstead. The directive names areServerNameandDocumentRooton Apache.- File: /etc/nginx/sites-available/example.com.conf
1 2server_name example.com www.example.com; root /var/www/html/example.com/public;
Create a symbolic link to the
sites-enableddirectory to enable the site.sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/example.com.conf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/Certbot is now a Snap package. To use Snap, install the
snapdpackage and initialize it.sudo apt install snapd sudo snap install coreRemove any old
certbotUbuntu packages to avoid conflicts. Usesnapto install a newcertbotpackage. Create a symbolic link to thecertbotdirectory.sudo apt remove certbot sudo snap install --classic certbot sudo ln -s /snap/bin/certbot /usr/bin/certbotUse
certbotto install a certificate for the domain. Add the--nginxoption to use the NGINX plugin. This option also edits the virtual host file to simplify the configuration process.Note To request a certificate without changing the virtual host settings, use thecertonlyoption, for example,sudo certbot certonly --nginx. To configure Apache, run the commandsudo certbot --apacheinstead.sudo certbot --nginxDuring the installation process, Certbot prompts for extra information including a email address and domain name. The following instructions apply to the configuration process.
- Enter an email address: Certbot requests an email address where it can send urgent notices about the domain or registration.
- Accept the terms of service: To agree to the terms, enter
Y.EnterNto terminate the certificate request. Use the link in the output to download the PDF file and review the terms. - Optionally subscribe to mailing list: Answer either
YorNwhen asked whether to subscribe to the EFF mailing list. This setting does not affect the rest of the installation. - Enter the domain name(s): Certbot requests one or more domain names for the certificate. Certbot displays the names of any eligible domains based on the contents of the virtual host files. Select the numbers corresponding to the relevant domains, including a space between each number. If the domain name does not appear, enter the domain name without the
httporhttpsprefix, for example,example.com. If there is more than one domain to certify, separate the names using either a space or a comma. Remember to request separate certificates with and without thewwwprefix for each domain.
Certbot contacts Let’s Encrypt to request the certificate(s) and perform any necessary challenges. In most cases, ownership can be proven through an HTTP challenge. If the operation is successful, Certbot confirms the successful grant request. It also displays some information about the certificates and key chains, along with the expiration date. Certificates typically expire in 90 days.
Requesting a certificate for example.com and www.example.com Successfully received certificate. Certificate is saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/fullchain.pem Key is saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/privkey.pem This certificate expires on 2023-02-28. These files will be updated when the certificate renews. Certbot has set up a scheduled task to automatically renew this certificate in the background. Deploying certificate Successfully deployed certificate for example.com to /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/example.com.conf Successfully deployed certificate for www.example.com to /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/example.com.conf Congratulations! You have successfully enabled HTTPS on https://example.com and https://www.example.comEdit the site configuration file at
/etc/nginx/sites-available/example.com.conf, using the sample file as a template. Make the following changes to the file:- Add the three
add_headerdirectives to the top of the file. - Add the string
index.htm index.phpto theindexdirective. - Add
/index.php?$query_stringto thetry_filesdirective inside thelocation /block. - Add
locationdirectives for/favicon.icoand/robots.txt. - Add the
error_page,charset, andclient_max_body_sizedirectives. - Add the
location ~ \.php$block. For thefastcgi_passdirective, change the filenamephp8.1-fpm.sockto reflect the PHP release. For example, if PHP release7.4is installed, the name of the file isphp7.4-fpm.sock. To confirm the PHP release, use thephp -vcommand. - Do not change any of the lines added by Certbot. This section begins with the line
listen [::]:443.
"Note For the Apache web server, add the configuration above to the/etc/apache2/sites-available/example.com.conffile. Many directive names are slightly different on Apache. See the Pixelfed Apache instructions or consult the Apache documentation for more information.- File: /etc/nginx/sites-available/example.com.conf
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51server { add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN"; add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block"; add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff"; server_name example.com example.com; root /var/www/html/example.com/public; index index.html index.htm index.php; location / { try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$query_string; } location = /favicon.ico { access_log off; log_not_found off; } location = /robots.txt { access_log off; log_not_found off; } charset utf-8; client_max_body_size 15M; # or your desired limit error_page 404 /index.php; # pass PHP scripts to FastCGI server # location ~ \.php$ { include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf; # With php-fpm (or other unix sockets): fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php8.1-fpm.sock; } listen [::]:443 ssl ipv6only=on; # managed by Certbot listen 443 ssl; # managed by Certbot ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/fullchain.pem; # managed by Certbot ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/example.com/privkey.pem; # managed by Certbot include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-nginx.conf; # managed by Certbot ssl_dhparam /etc/letsencrypt/ssl-dhparams.pem; # managed by Certbot } server { if ($host = www.example.com) { return 301 https://$host$request_uri; } # managed by Certbot if ($host = example.com) { return 301 https://$host$request_uri; } # managed by Certbot listen 80; listen [::]:80; server_name example.com www.example.com; return 404; # managed by Certbot }
- Add the three
Test the NGINX configuration. If no errors are found, reload NGINX.
sudo nginx -t sudo systemctl reload nginx
Install and Configure Pixelfed
Install Pixelfed
The LEMP/LAMP stack and all settings are now ready to support Pixelfed. Clone and download Pixelfed using git.
Change to the
rootdirectory for the domain at/var/www/html/example.com. Substitute the actual domain name forexample.com.cd /var/www/html/example.com/Use
gittoclonethe Pixelfed files.git clone -b dev https://github.com/pixelfed/pixelfed.git .Recursively set the owner and permissions for the new directories.
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data . sudo find . -type d -exec chmod 755 {} \; sudo find . -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \;
Configure Pixelfed
Use the composer tool to initialize and configure PHP. Additionally, changes must be made to the .env file. For more in-depth information about the Pixelfed configuration, see the Pixelfed Documentation
.
From the same directory, use
composerto initialize the PHP settings for Pixelfed.sudo composer install --no-ansi --no-interaction --optimize-autoloaderCreate a new copy of the sample
.envfile.sudo cp .env.example .envEdit the
.envfile and edit the following server variables. Leave the other variables set to their current values.APP_NAME: This is the title to display in the header bar and elsewhere throughout the application.
APP_ENV: This should be set to
debugfor a test environment andproductionotherwise.APP_DEBUG: This should be set to
truefor debugging andfalseotherwise.APP_URL: This field contains the HTTP URL for the Pixelfed domain, for example,
https://example.com.APP_DOMAIN: Set this to the domain name without the HTTPS prefix. For the URL above, this is
example.com.ADMIN_DOMAIN: Set this to the domain name.
SESSION_DOMAIN: Set this to the domain name.
DB_CONNECTION: For MySQL and MariaDB databases set this to
mysql.DB_HOST: Set this to
127.0.0.1.DB_PORT: This is
3306for MySQL and MariaDB installations.DB_DATABASE: Set this to
pixelfed.DB_USERNAME: Set this to
pixelfed.DB_PASSWORD: Specify the password provided when creating the
pixelfeduser.vi .env
- File: /var/www/html/example.com/.env
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15APP_NAME="Pixelfed Demo" APP_ENV=production APP_URL=https://example.com APP_DOMAIN="example.com" ADMIN_DOMAIN="example.com" SESSION_DOMAIN="example.com" TRUST_PROXIES="*" DB_CONNECTION=mysql DB_HOST=127.0.0.1 DB_PORT=3306 DB_DATABASE=pixelfed DB_USERNAME=pixelfed DB_PASSWORD=<Database_Password>
(Optional) By default, Pixelfed does not send emails. To allow Pixelfed to send emails, change the
MAIL_variables in.envto the correct mail server settings. See the Pixelfed Email Settings example for instructions.
Run the Pixelfed Installation Scripts
Pixelfed does not use a single set-up script. It is necessary to run a large number of php artisan commands to configure the different parts of the system. To run the install scripts, follow the steps below:
Change to the domain root directory and generate the secret key. In the following example, change
example.comto the name of the domain.cd /var/www/html/example.com sudo php artisan key:generateINFO Application key set successfully.Link the application storage directory.
sudo php artisan storage:linkINFO The [public/storage] link has been connected to [storage/app/public].Migrate the database.
sudo php artisan migrate --forceImport the city data set to enable support for location data.
sudo php artisan import:citiesSuccessfully imported 128769 entries!Cache the Pixelfed routes and views to allow for better performance.
php artisan route:cache php artisan view:cacheINFO Routes cached successfully. INFO Blade templates cached successfully.Cache the Pixelfed configuration.
Note Run this command each time the.envfile changes.sudo php artisan config:cacheINFO Configuration cached successfully.Enable the Horizon dashboard and job queueing.
Note Pixelfed supports other queueing methods, buthorizonis the most straightforward. Consult the Pixelfed documentation for more details.sudo php artisan horizon:install sudo php artisan horizon:publishHorizon scaffolding installed successfully. INFO Publishing [horizon-assets] assetsAdd a cron job to regularly schedule the clean-up task. Open the root
crontabfile.sudo crontab -eAdd the following crontab entry to the bottom of the file.
* * * * * /usr/bin/php /usr/share/webapps/pixelfed/artisan schedule:run >> /dev/null 2>&1
Enable the Pixelfed Service in Systemctl
The easiest way to start and stop Pixelfed is to run it as a systemctl service. To add Pixelfed to the system daemon, follow the steps below:
Create a service entry file named
pixelfed.servicein/etc/systemd/system.sudo vi /etc/systemd/system/pixelfed.serviceAdd the following service description. For the
ExecStartparameter, replaceexample.comwith the actual name of the domain.Note Apache users should changerequires=nginxtorequires=apache.- File: /etc/systemd/system/pixelfed.service
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15[Unit] Description=Pixelfed task queueing via Laravel Horizon After=network.target Requires=mariadb Requires=php-fpm Requires=redis Requires=nginx [Service] Type=simple ExecStart=/usr/bin/php /var/www/html/example.com/artisan horizon Restart=on-failure [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Enable the service using
systemctl enable.sudo systemctl enable --now pixelfedRestart the service and verify it is active.
sudo systemctl restart pixelfed.service sudo systemctl status pixelfed.servicepixelfed.service - Pixelfed task queueing via Laravel Horizon Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/pixelfed.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Thu 2022-12-01 10:24:42 UTC; 3s ago
Create a Pixelfed Administrator and Use the Pixelfed Web Interface
To access the Pixelfed administration dashboard, first create an administrative account using the php artisan user:create command. Additional user accounts can be created using the Pixelfed web interface. Follow the steps below to create an administrator account.
Change to the root directory of the Pixelfed domain. Run the
artisanaccount creation script. In the following example, replaceexample.comwith the name of the domain.cd /var/www/html/example.com sudo php artisan user:createWhen prompted, provide the following information.
- Name: This is the public-facing name for the account.
- Username: This is the internal name of the account.
- Email: This is the email address for the account.
- Password/Confirm Password: Provide a secure password for the account.
- Make this user an admin? (yes/no): Answer
yesto create an administrative account. - Manually verify email address? (yes/no): It is safe to answer
noin this case because the account is being created internally. To answeryes, email must be enabled on both Pixelfed and Linode. - Are you sure you want to create this user? (yes/no): Answer
yesto create the user of the account.
Created new user!Using a web browser, navigate to the site domain name. The browser should display the Pixelfed login page. Enter the administrator email address and password.

Pixelfed displays the home page for the account.
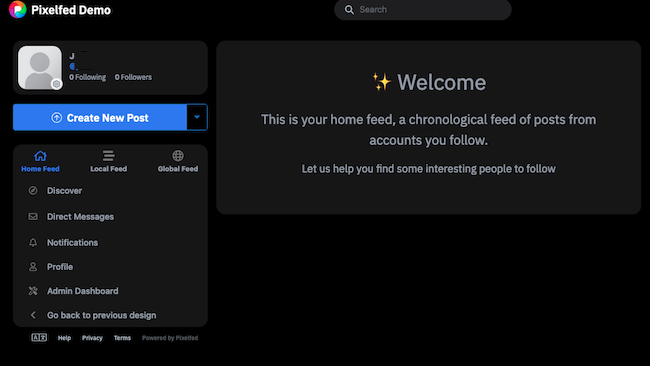
To access the administration dashboard, click Admin Dashboard on the left-hand menu. When prompted, enter the account password. Pixelfed displays the dashboard.

For more information on using or administering Pixelfed, consult the Pixelfed documentation .
Conclusion
Pixelfed is a federated open-source application for sharing photos, art, and videos. Each Pixelfed server is operated independently as part of a distributed network with no central authority. Pixelfed is free to use and can be downloaded using git. Pixelfed requires a LAMP or LEMP stack, along with several other helper applications. To install and configure Pixelfed, use the composer and artisan scripts. Administrator accounts must also be created beforehand using a console. The Pixelfed web portal allows other users to create accounts, while administrators can manage the site using the Pixelfed Dashboard. For more information on administering a Pixelfed server, see the Pixelfed documentation
.
More Information
You may wish to consult the following resources for additional information on this topic. While these are provided in the hope that they will be useful, please note that we cannot vouch for the accuracy or timeliness of externally hosted materials.
This page was originally published on
