This blog was written in collaboration with Ulhas Math, whose expertise as a Senior Architect for Cloud Wrapper defined the architectural evolution and performance improvements outlined below. His guidance was instrumental in addressing the scaling challenges posed by small-object web traffic.
Cloud Wrapper launched in 2018 as Akamai’s dedicated caching solution, custom-built for large media objects. At the time, our media customers needed better offload in the face of increasing egress costs for their ever-growing streaming libraries.
Cloud Wrapper delivered on this need and grew from an added benefit with the overall goal of fetching an object once, to a critical component of large media customers’ Content Delivery infrastructure. We now see customers leveraging Cloud Wrapper to reduce costs when building disaster recovery solutions, and it has now become the standard for live streaming customers. It offers origin shielding during high-traffic events, multi-CDN capabilities, and delivers a dedicated cache that customers, including Roku, can rely on across all third-party CDNs.
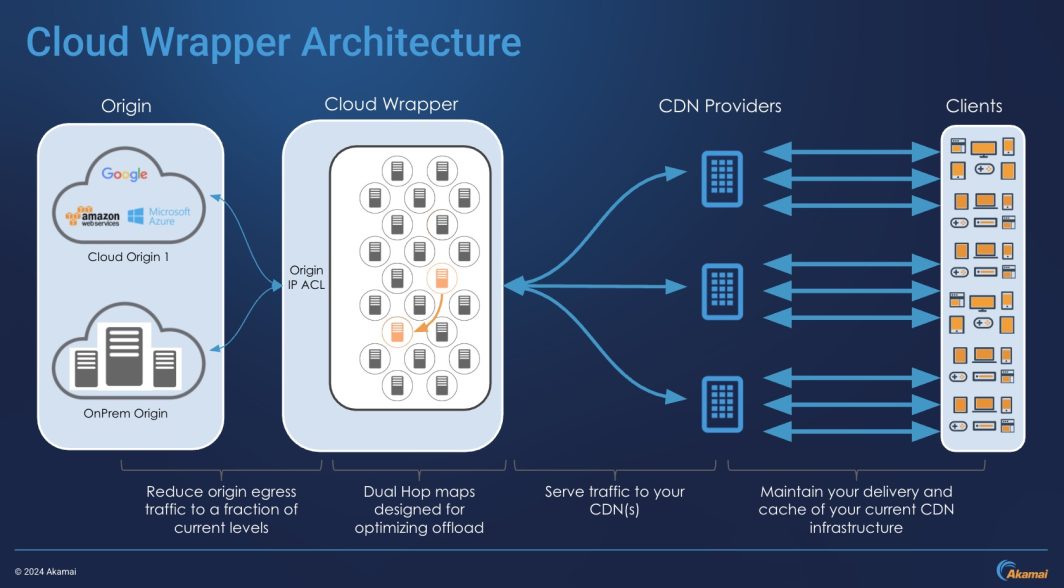
In September 2024, we expanded Cloud Wrapper to support small objects and web assets.
Adapting to Web Content
While Cloud Wrapper was purpose-built for large media objects, offload and origin shielding is not just a media-specific problem. Customers with many other use cases, such as e-commerce businesses with thousands of product photos and other asset-heavy applications, were requesting Cloud Wrapper to cache their web assets for a reduction in cloud egress costs and improved performance (resulting in improved SEO rankings). However, web assets are significantly smaller than media objects. Cloud Wrapper’s caching ethos would meet customers’ needs, but the product faced issues when trying to treat a tiny web asset (~0.030MB) like a large media object (~1.90MB).
We needed to improve Cloud Wrapper so it could handle small (and only getting smaller) objects, ensuring that the solution was high-performance, able to scale, and optimized to handle a higher eviction rate on its dedicated servers.
Scaling Cloud Wrapper for Small-Object Web Performance
As web experiences become increasingly dynamic and asset-heavy, ensuring consistent performance across both small-object web traffic and large media files is more critical than ever. Cloud Wrapper has long been a cornerstone for high-performance content delivery, particularly for large media workflows. But as customer needs evolved, we needed to re-architect parts of the system to handle a new challenge: efficiently caching and delivering a massive number of small web objects without sacrificing speed or scale.
Separating Traffic to Preserve Performance
Mixing small-object web traffic with large media assets was found to degrade performance for both types of workloads. To address this, we created a separate deployment of Cloud Wrapper servers specifically for web traffic. This separation allowed each deployment to be optimized for its unique workload, ensuring consistent performance regardless of object size.
We also upgraded the infrastructure for this new deployment by selecting high-performance hardware with SSD disks, similar to the ones already proven to handle Edge traffic at Akamai scale.
Scaling to Handle Millions More Objects
In traditional media use cases, disk space was the primary constraint, so we had to ensure enough storage for massive video files and media assets. But with small objects like HTML fragments, JSON files, and API responses, we encountered a different bottleneck: the number of objects a server could store and manage.
To support this shift, we updated our core caching services to handle nearly 3x the number of objects that earlier versions of Cloud Wrapper could support. This upgrade dramatically increased our object density per server, enabling us to meet the needs of web-first customers while improving overall infrastructure efficiency.
Improving Eviction Handling for Fair and Fast Caching
Cloud Wrapper’s architecture is built on the principle of funneling requests through a smaller set of servers to maximize cache effectiveness. However, this design also meant that a single server had to ingest and manage an enormous volume of small objects during traffic spikes or frequent deployments.
Each customer has a dedicated cache quota, which means that as new content flows in, older content must be evicted at the same pace to maintain fairness and consistency. To support this, we enhanced our eviction mechanisms, ensuring that servers could efficiently and reliably clear space without impacting cache hit rates or slowing down delivery.
Results
With these architectural improvements, Cloud Wrapper now serves as a high-performance origin shield for everything from tiny web assets to massive media files. Our goal remains simple: fetch every object only once.
For small-object web traffic, customers saw a 5–10% improvement in offload, with some achieving offload rates of over 99%. This means fewer origin requests, faster response times, and lower infrastructure costs.
Today, Cloud Wrapper remains the market-leading origin shield. Learn more about how Cloud Wrapper can improve your web performance here.








Comments